41 fluorescent labels and light microscopy
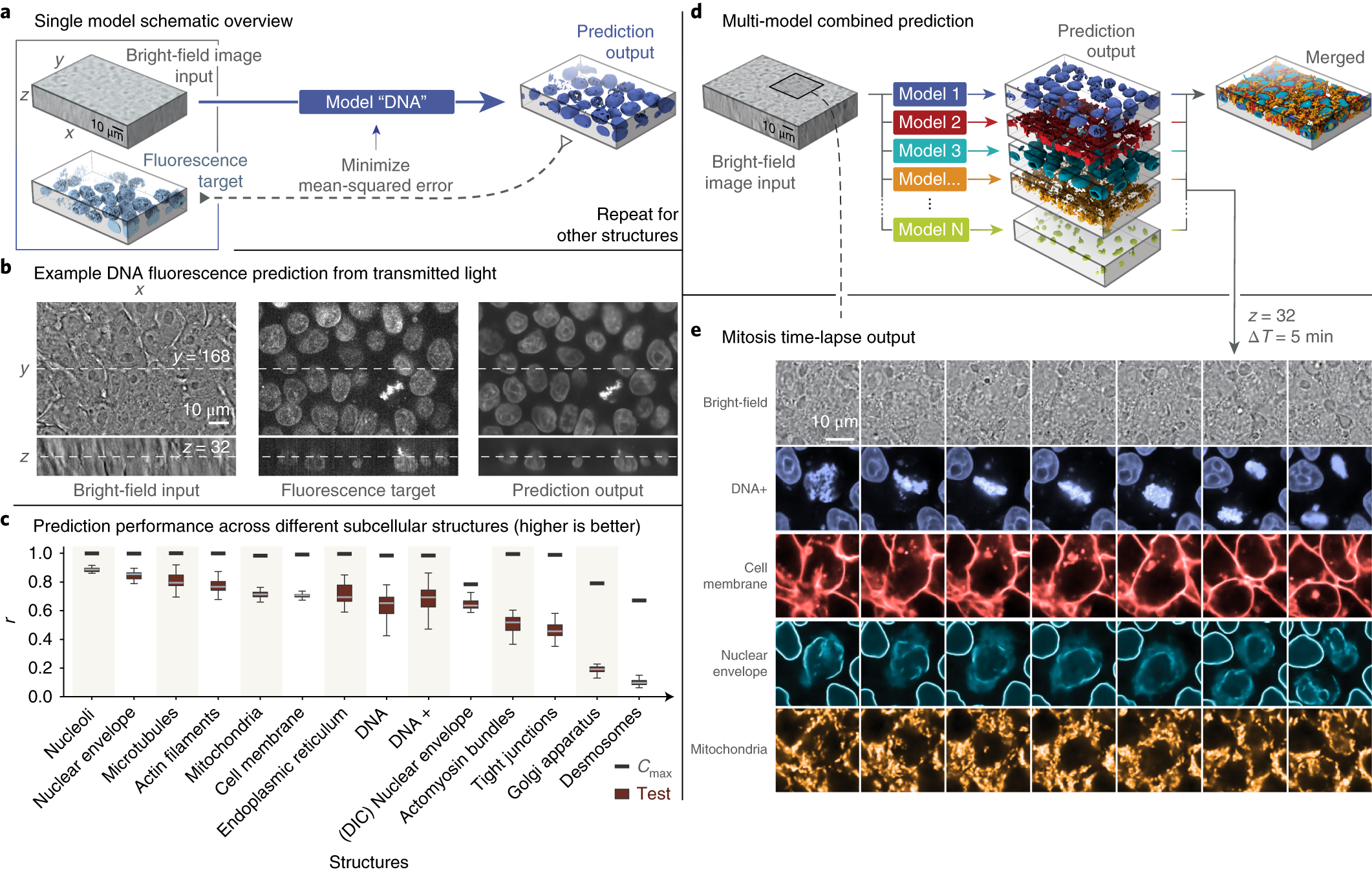
Fluorescence Microscopy - Explanation and Labelled Images Fluorescence microscopy uses a high-intensity light source that excites a fluorescent molecule called a fluorophore in the sample observed. The samples are labeled with fluorophore where they absorb the high-intensity light from the source and emit a lower energy light of longer wavelength. Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from ... Although fluorescence microscopy can resolve subcellular structure in living cells, it is expensive, is slow, and can damage cells. We present a label-free method for predicting three-dimensional...
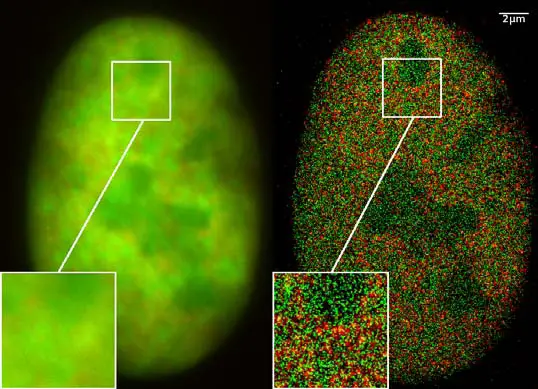
New fluorescent label provides a clearer picture of how DNA ... Unlike traditional fluorescence microscopy, which uses labels that glow constantly, this approach involves switching on only a subset of the labels at each moment.

Fluorescent labels and light microscopy
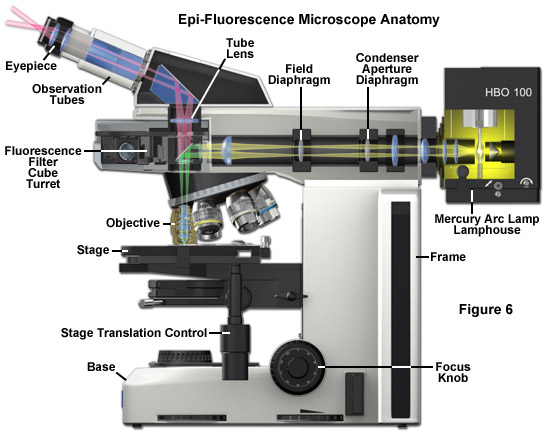
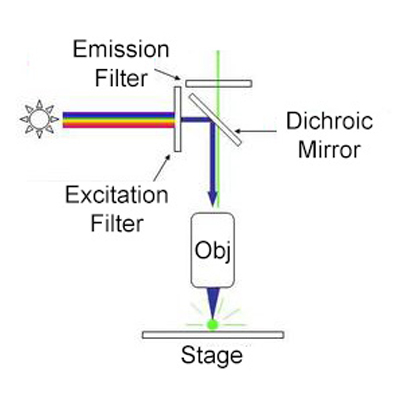
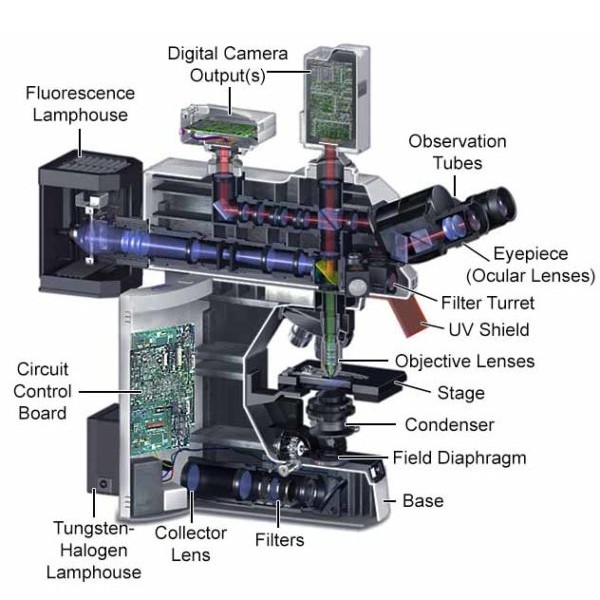
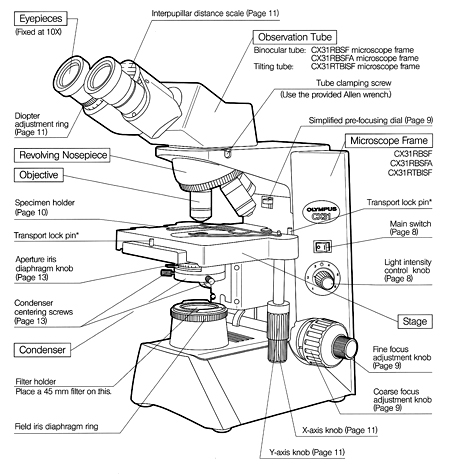
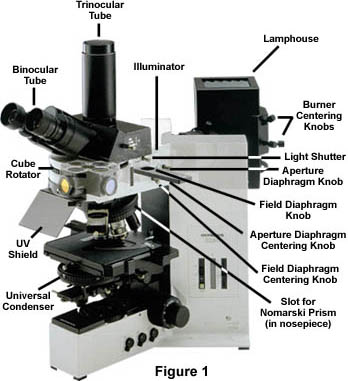
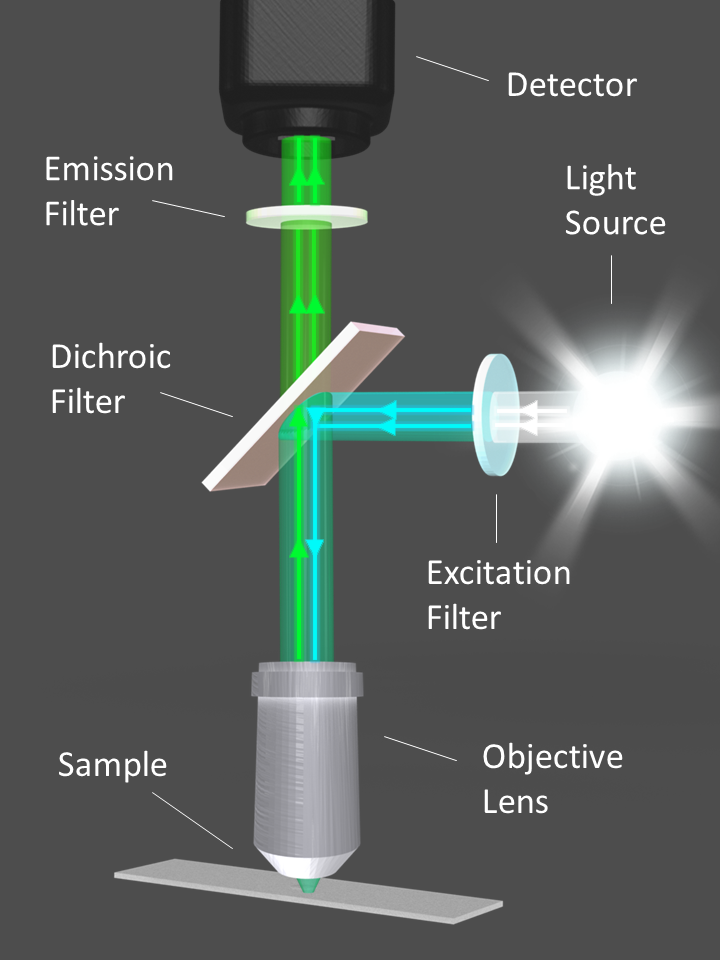
Fluorescence Microscope: Principle, Types, Applications Fluorescence microscopy is a light microscope that works on the principle of fluorescence. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation (such as UV light) and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light (such as green or red light). Fluorescence microscope - Wikipedia The majority of fluorescence microscopes, especially those used in the life sciences, are of the epifluorescence design shown in the diagram.Light of the excitation wavelength illuminates the specimen through the objective lens. The fluorescence emitted by the specimen is focused to the detector by the same objective that is used for the excitation which for greater resolution will need ... Light Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram ... A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.
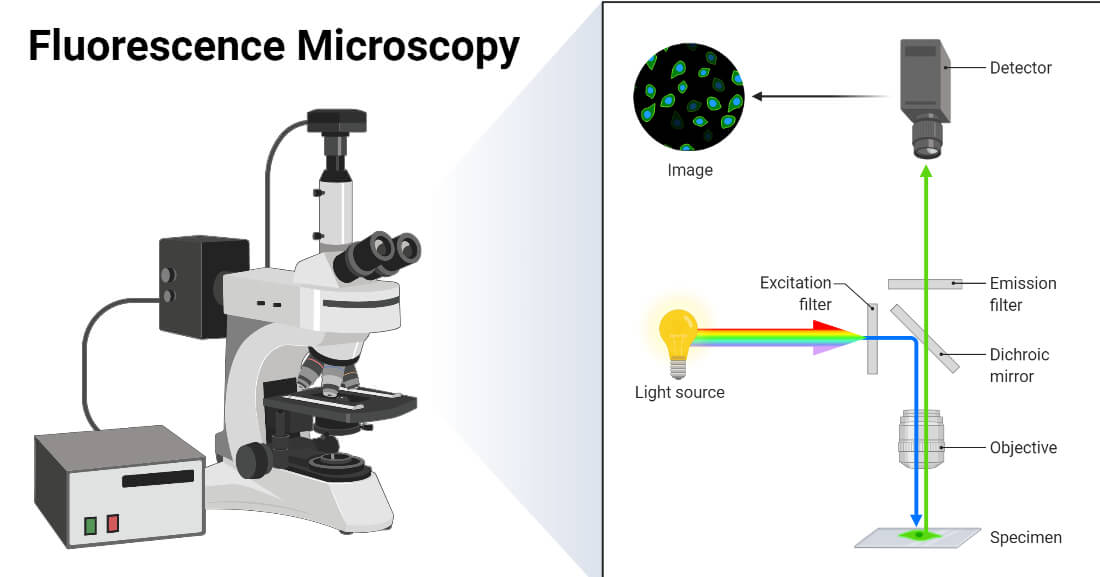
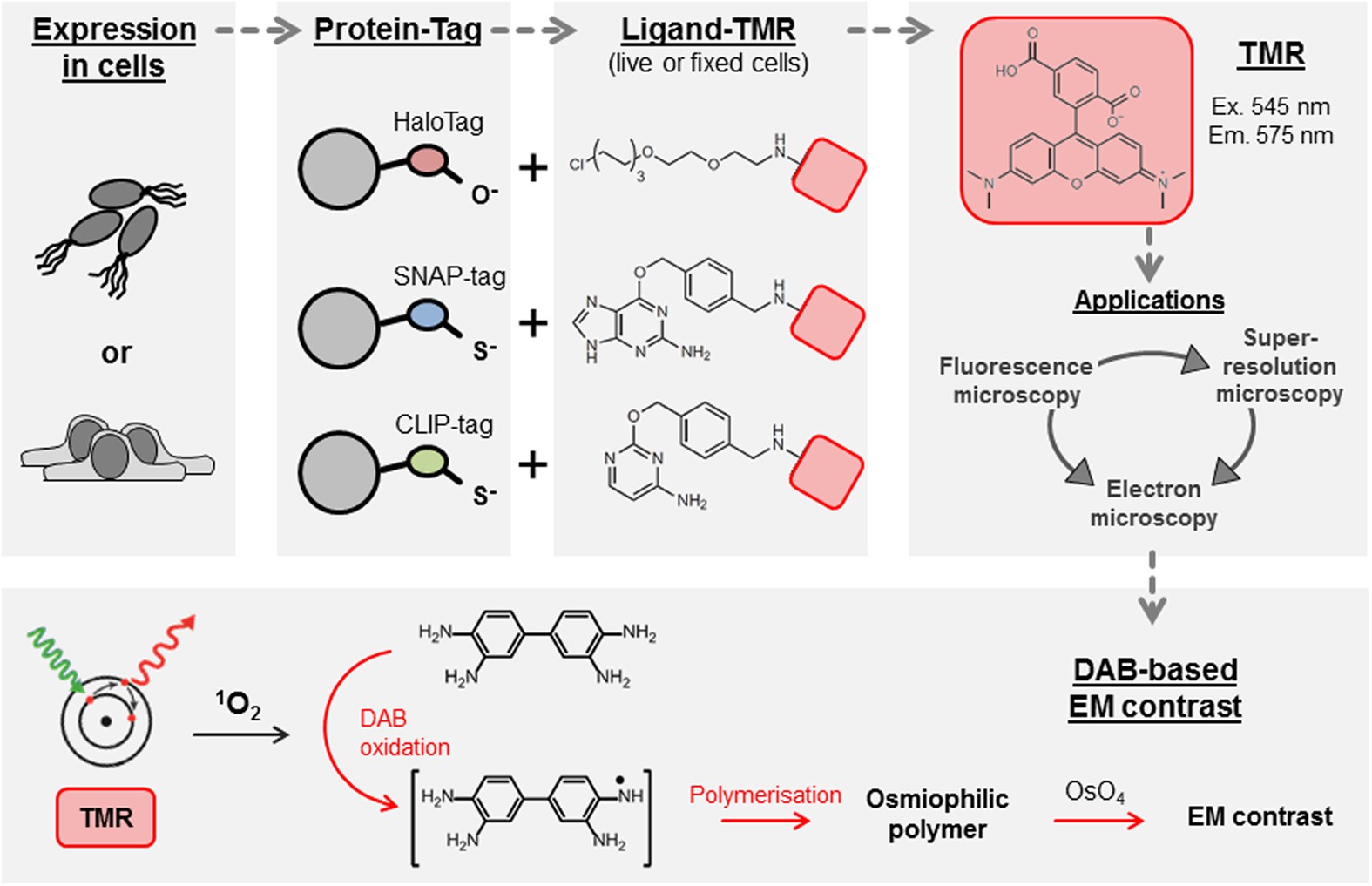
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy. Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy | Nikon's MicroscopyU It is important to note that fluorescence is the only mode in optical microscopy where the specimen, subsequent to excitation, produces its own light. The emitted light re-radiates spherically in all directions, regardless of the excitation light source direction. Novel Fluorescent Label Shines a Light on DNA Structure in Cancer Cells Novel Fluorescent Label Shines a Light on DNA Structure in Cancer Cells March 7, 2022 Researchers have developed a new fluorescent label that gives a clearer picture of how DNA architecture is... › science-lab › fret-withFRET with FLIM | Science Lab | Leica Microsystems Aug 07, 2012 · FLIM combines lifetime measurements with imaging: lifetimes obtained for each image pixel are color-coded to produce additional image contrast. Thus, FLIM delivers information about the spatial distribution of a fluorescent molecule together with information about its biochemical status or nano-environment. A typical application of FLIM is FLIM-FRET. FRET is a well-established technique to ... Different Ways to Add Fluorescent Labels - Thermo Fisher Scientific Fluorescent labeling methods can vary Using fluorescent dyes as functional indicators Important characteristics of fluorescent dyes Using fluorescence to detect your target Using fluorescence provides greater contrast compared to viewing your samples with brightfield microscopy alone.
Labeling the ER for Light and Fluorescence Microscopy Labeling the ER for Light and Fluorescence Microscopy Chris Hawes, Pengwei Wang & Verena Kriechbaumer Protocol First Online: 17 October 2017 1708 Accesses 4 Citations Part of the Methods in Molecular Biology book series (MIMB,volume 1691) Abstract The ER is a highly dynamic network of tubules and membrane sheets. Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from ... Although fluorescence microscopy can resolve subcellular structure in living cells, it is expensive, is slow, and can damage cells. We present a label-free method for predicting three-dimensional fluorescence directly from transmitted-light images and demonstrate that it can be used to generate multi-structure, integrated images. ZEISS Lightsheet 7 - Light Sheet Microscope This effect occurs in all fluorescence microscopes, but the illumination axis in light sheet fluorescence microscopy is perpendicular to the observation axis and so this effect is more obvious. ... The labels are yellow: GFP-CD8 T cells, cyan: B220 (B Cell Follicles, Alexa555), magenta: CD31 (Vasculature, Alexa647) Fluorescence Microscopy vs. Light Microscopy - News-Medical.net This means that fluorescent microscopy uses reflected rather than transmitted light. For example, a commonly used label is green fluorescent protein (GFP), which is excited with blue light and...
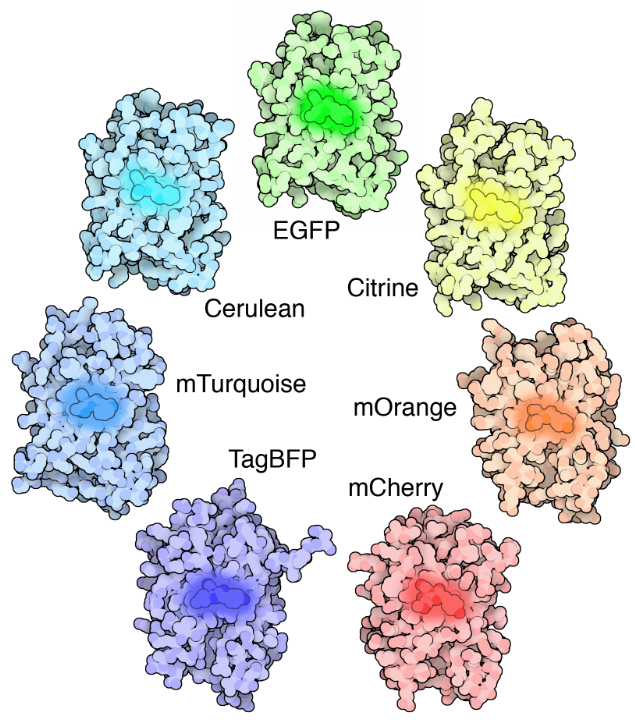
Fluorescence Microscopy - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) Second harmonic (blue) or fluorescence (green) light are transmitted and collected by PMTs after separation by a dichroic mirror (DM). Two-photon light is transmitted by the DM to produce a transmitted light image. Reflected fluorescence is detected after DM ( bottom right image). Fluorescence Imaging - Teledyne Photometrics Fluorescent molecules (known as fluorophores) are used to label samples, and fluorophores are available that emit light in virtually any color. In a fluorescent microscope, a sample is labeled with a fluorophore, and then a bright light ( excitation light) is used to illuminate the sample, which gives off fluorescence ( emission light ). Dots, Probes and Proteins: Fluorescent Labels for Microscopy and Imaging GFP now comes in 'flavors' including cyan, yellow and blue. Fluorescent proteins are useful for studying live cells and can be used as 'reporters' for studying gene expression. Using genetically modified plasmid and/or viral DNA, the target cells can be transfected with the plasmid which encodes both the fluorescent protein and a gene ... Fluorescence Microscopy & Cell Imaging | Research | UNM Cancer Center The Fluorescence Microscopy and Cell Imaging Shared Resource aids basic and physician researchers to image samples and publish high profile articles that: Elucidate cell and molecular mechanisms of cancer, immunologic, infectious, metabolic, neurologic and vascular diseases. Evaluate therapeutic efficacy in cells and patient samples.
What do researchers use fluorescent labels and light microscopy for ... What do reseaches use fluorescent labels and light microscopy to do? A) produce movies of cells as they grow, divide and develop B) scan cells with laser beans C) follow molecules moving through ...
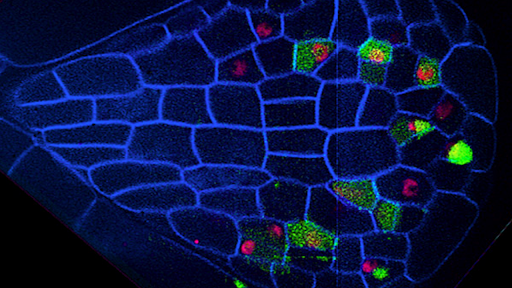
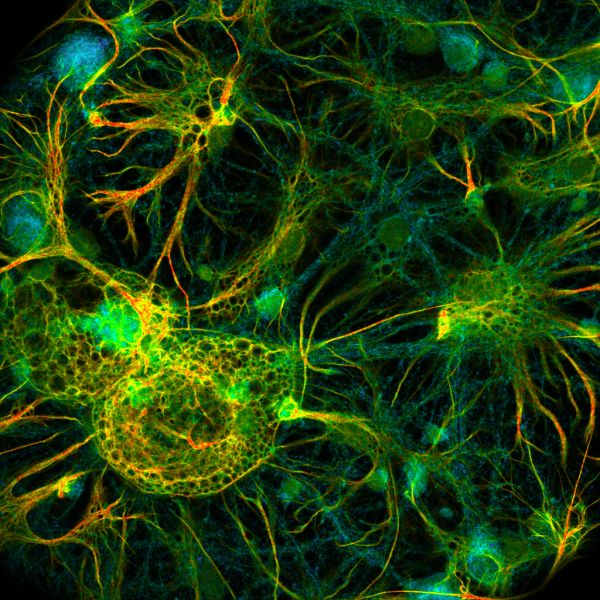
Fluorescent Microscopy Fluorescent microscopy is often used to image specific features of small specimens such as microbes. It is also used to visually enhance 3-D features at small scales. This can be accomplished by attaching fluorescent tags to anti-bodies that in turn attach to targeted features, or by staining in a less specific manner.
Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fluorescence microscopy is a technique whereby fluorescent substances are examined in a microscope. It has a number of advantages over other forms of microscopy, offering high sensitivity and specificity. In fluorescence microscopy, the specimen is illuminated (excited) with light of a relatively short wavelength, usually blue or ultraviolet (UV).
› open-accessOpen Access | Open Access Publications » A complete version of the work and all supplemental materials, including a copy of the permission as stated above, in a suitable standard electronic format is deposited immediately upon initial publication in at least one online repository that is supported by an academic institution, scholarly society, government agency, or other well-established organization that seeks to enable Open ...
Fluorescent tag - Wikipedia The fluorophore selectively binds to a specific region or functional group on the target molecule and can be attached chemically or biologically. [1] Various labeling techniques such as enzymatic labeling, protein labeling, and genetic labeling are widely utilized. Ethidium bromide, fluorescein and green fluorescent protein are common tags.
› createJoin LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
› scitable › topicpageFluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) | Learn Science at ... Soon after Gall and Pardue's work, fluorescent labels quickly replaced radioactive labels in hybridization probes because of their greater safety, stability, and ease of detection (Rudkin ...
Fluorescence microscopy: established and emerging methods ... - PubMed The primary concern in all forms of microscopy is the generation of contrast; for fluorescence microscopy contrast can be thought of as the difference in intensity between the cell and background, the signal-to-noise ratio. High information-content images can be formed by enhancing the signal, suppressing the noise, or both.
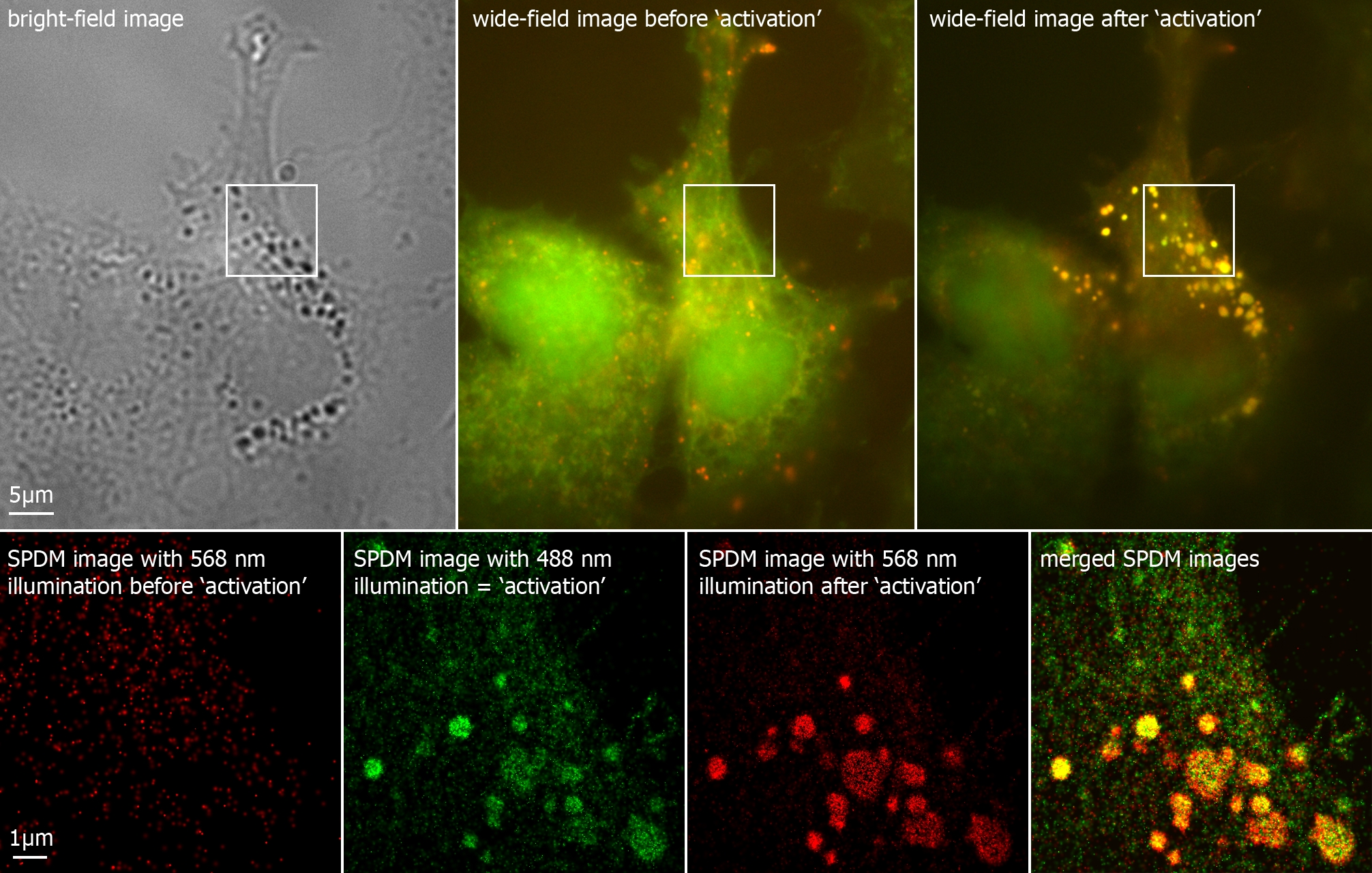
› doi › 10Imaging Intracellular Fluorescent Proteins at Nanometer ... Sep 15, 2006 · Early results in single-molecule microscopy and the spatiospectral isolation of individual exciton recombination sites in a semiconductor quantum well led to a proposal for a means of molecular resolution fluorescence microscopy a decade ago . In brief, individual molecules densely packed within the resolution limit of a given instrument [as ...
Fluorescent Labeling - What You Should Know - PromoCell Fluorescence microscopy allows the identification of cells and cellular components and the monitoring of cell physiology with high specificity. Fluorescence microscopy separates emitted light from excitation light using optical filters. The use of two indicators also allows the simultaneous observation of different biomolecules at the same time.
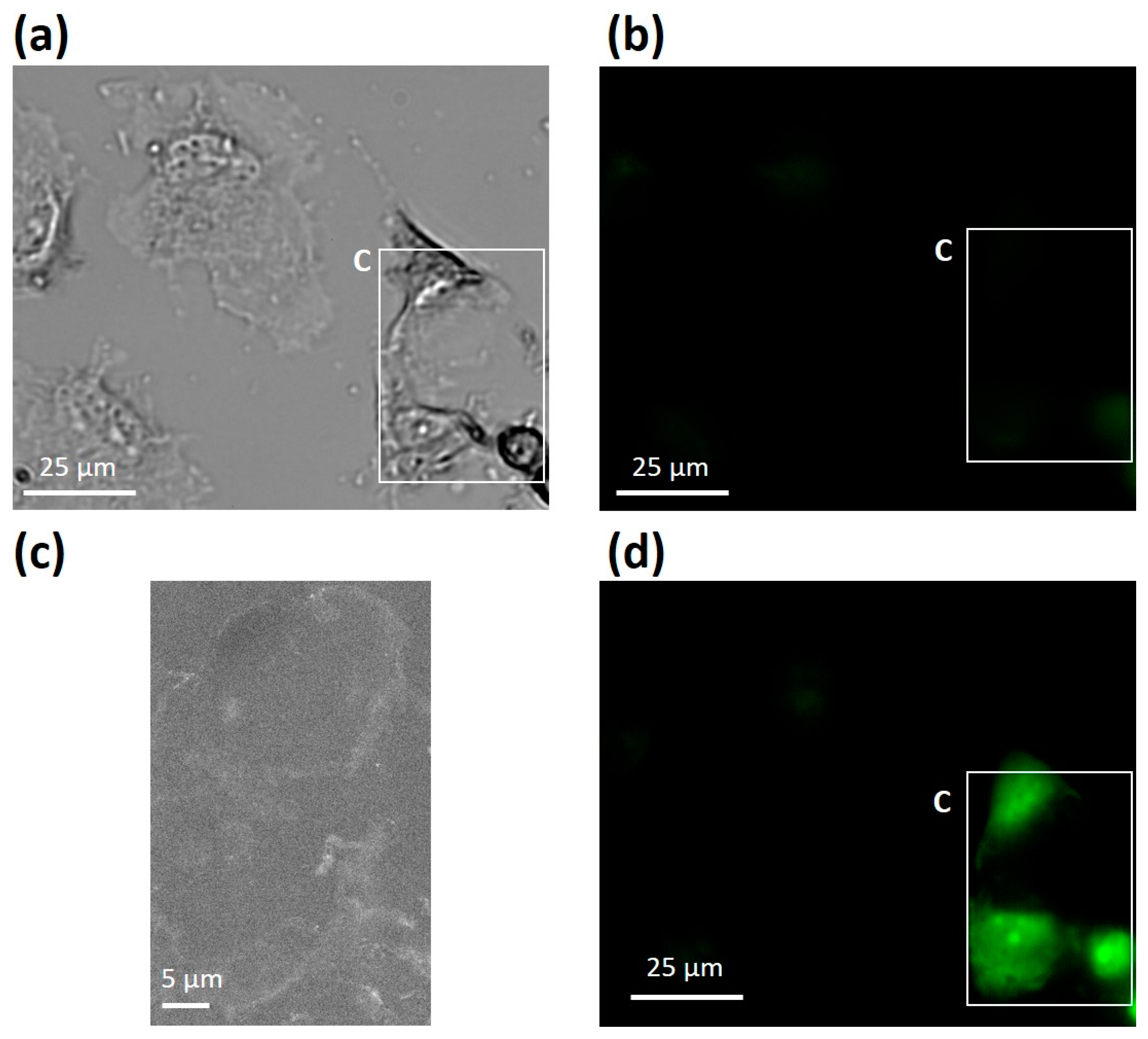
Fluorescent labeling of abundant reactive entities (FLARE) for cleared ... Fluorescence microscopy is a vital tool in biomedical research but faces considerable challenges in achieving uniform or bright labeling. For instance, fluorescent proteins are limited to model ...
› microscopy › enZEISS Axioscan 7 Microscope Slide Scanner Digitize your specimens with Axioscan 7 – the reliable, reproducible way to create high-quality virtual microscope slides. Axioscan 7 combines qualities that you would not expect to get in a slide scanner: high speed digitization and outstanding image quality plus an unrivaled variety of imaging modes are all available in a fully automated and easy to operate system.
Fluorescence Live Cell Imaging - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) Fluorescent protein tags, live cell dyes, and other methods to fluorescently label proteins of interest provide a range of tools to investigate virtually any cellular process under the microscope. The two main experimental challenges in collecting meaningful live cell microscopy data are to minimize photodamage while retaining a useful signal ...
Localizing Molecules in Plant Cell Walls Using Fluorescence Microscopy ... Fluorescent labels are available in a wide range of emission wavelengths typically using Alexa dyes. Alexa 633 completely avoids overlap with lignin autofluorescence or counterstains such as calcofluor or acriflavin.
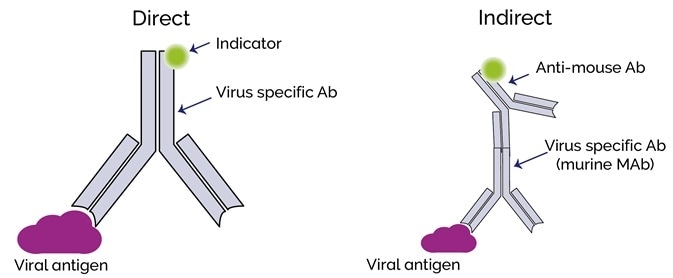
Fluorescent Dyes | Science Lab | Leica Microsystems In fluorescence microscopy there are two ways to visualize your protein of interest. Either with the help of an intrinsic fluorescent signal - by genetically linking a fluorescent protein to a target protein - or with the help of fluorescently labeled antibodies that bind specifically to a protein of interest.
Labeling Proteins For Single Molecule Imaging - Teledyne Photometrics A fluorescent signal allows a protein's precise location to be determined as well as its behavior to be observed. This can then be studied in relation to other fluorescently tagged proteins. In this way, researchers are able to use fluorescence microscopy to visualize underlying biological processes.
Label-Free Fluorescence Microscopy Through Channels Now, researchers in Sweden have developed a new technique called nanofluidic scattering microscopy, which images the target particles while they are flowing through an optically transparent matrix of nanoscale channels (Nat. Methods, doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01491-6 ). The technique, which incorporates dark-field light-scattering microscopy ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ImmunofluorescenceImmunofluorescence - Wikipedia Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample.
Light Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram ... A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.
Fluorescence microscope - Wikipedia The majority of fluorescence microscopes, especially those used in the life sciences, are of the epifluorescence design shown in the diagram.Light of the excitation wavelength illuminates the specimen through the objective lens. The fluorescence emitted by the specimen is focused to the detector by the same objective that is used for the excitation which for greater resolution will need ...
Fluorescence Microscope: Principle, Types, Applications Fluorescence microscopy is a light microscope that works on the principle of fluorescence. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation (such as UV light) and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light (such as green or red light).








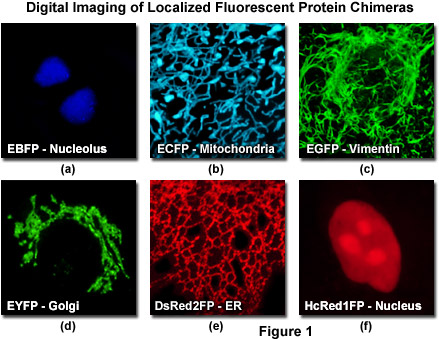







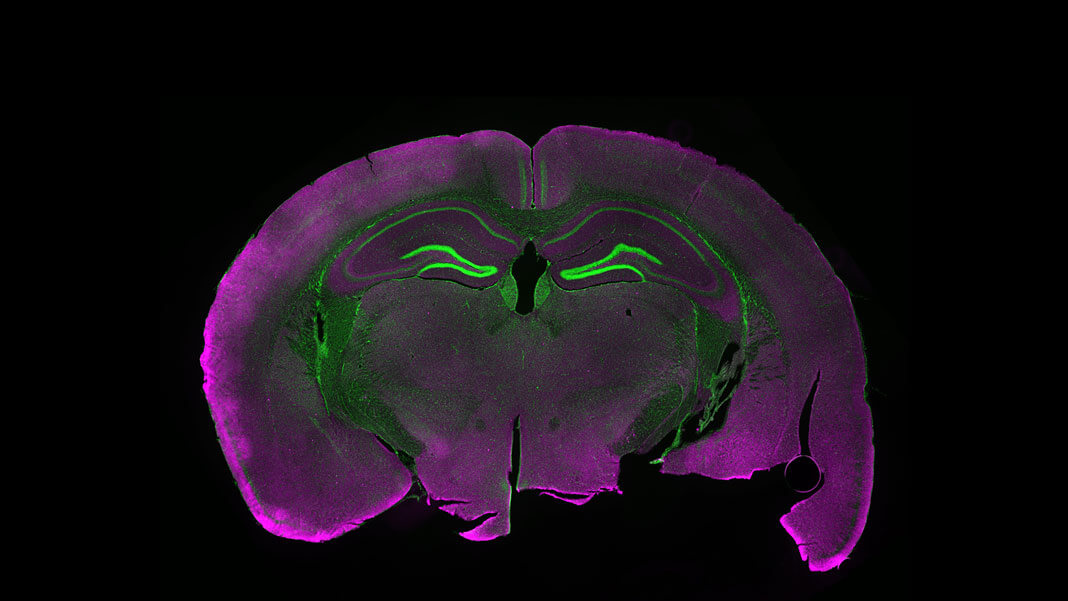


Post a Comment for "41 fluorescent labels and light microscopy"